Tuberculosis (TB) Tests - Tests for diagnosis of TB, sputum test, blood test
Nov 30, 2019
There are different types of TB tests available to diagnose TB. There are also TB tests to find out if someone has TB bacteria that are susceptible to TB drug treatment. If the bacteria are susceptible to treatment, it means that the treatment should work. The opposite of being susceptible to treatment is being drug resistant. A TB test to find out if someone has drug resistant TB, is known as a drug susceptibility test.
Even if a person has symptoms of TB it is often difficult to diagnose TB, and it is particularly difficult to diagnose it rapidly. Rapid diagnosis is what is needed to provide effective treatment for drug resistant TB.
Evidence of TB bacteria
Book a Home Visit Blood Test in Saki Naka
Book a Home Visit Blood Test in Borivali
Book a Home Visit Blood Test in Kajupada
Book a Home Visit Blood Test in Jogeshwari
Book a Home Visit Blood Test in Bandra
Book a Home Visit Blood Test in Kalyan
Book a Home Visit Blood Test in Vashi
Book a Home Visit Blood Test in Mulund
Book a Home Visit Blood Test in Belapur
Book a Home Visit Blood Test in Dombivli East
Book a Home Visit Blood Test in Dombivli West
Book a Home Visit Blood Test in Thane
Book a Home Visit Blood Test in Kharghar
Book a Home Visit Blood Test in Goregaon
Book a Home Visit Blood Test in Navi Mumbai
Book a Home Visit Blood Test in Andheri West
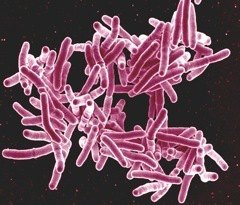
TB tests look for evidence of these TB bacteria, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, © NIAID
The development of TB disease is a two-stage process. In the first stage, known as latent TB, a person is infected with TB bacteria. In the second stage, known as active TB or TB disease, the bacteria have reproduced sufficiently to usually cause the person to become sick. Some tests are for latent TB, others are for active TB, and some are for both.
A diagnosis of active TB disease can only be confirmed when there is definite evidence of TB bacteria in the person’s body. Some of the TB tests, such as the skin test, look directly for TB bacteria. Others such as the chest X-ray look for the effect of the bacteria on the person suspected of having TB
The accuracy of TB tests
Some of the current tests take a long time to obtain a result, and some tests are not very accurate. The tests either have low sensitivity (the ability to correctly detect people with TB) and/or low specificity (the ability to correctly detect people who haven’t got TB).
If a TB test has low sensitivity, it means that there will be a significant number of “false negatives”, meaning that the test result is suggesting that a person has not got TB when they actually have. Similarly, a low specificity means that there will be a significant number of “false positives” suggesting that a person has TB when they actually don’t.
The most accurate tests such as culture take a long time to do. Some tests are also very expensive and require complex laboratory facilities.
Culture Test
Although the culture test for TB is very accurate, it can take several weeks to get a result. It also requires expensive equipment and skilled personnel.
Reporting Takes 6 weeks – 1320 MRPDifferent culture tests:
| SP60934 | AFB isolation by rapid culture using BACTEC MGIT BAL & other respiratory samples | Automated BACTEC MGIT 960 | Full bronchial lavage in sterile container |
| SP65467 | AFB isolation by rapid culture using BACTEC MGIT Blood | Automated BACTEC MGIT 960 | 3-5 ml of blood in BACTEC Myco / F Lytic bottle |
| SP60926 | AFB isolation by rapid culture using BACTEC MGIT Body Fluid | Automated BACTEC MGIT 960 | Body fluid in sterile container |
| SP70035 | AFB isolation by rapid culture using BACTEC MGIT Bone Marrow | Automated BACTEC MGIT 960 | 1-2 ml of bone marrow in BACTEC Myco / F Lytic bottle |
| SP60818 | AFB isolation by rapid culture using BACTEC MGIT CSF | Automated BACTEC MGIT 960 | CSF in sterile container (min 2 ml) |
| SP70036 | AFB Isolation by rapid culture using BACTEC MGIT Endometrium | Automated BACTEC MGIT 960 | Endometrium sample In sterile saline |
| SP70037 | AFB isolation by rapid culture using BACTEC MGIT Other samples | Automated BACTEC MGIT 960 | Other sample in sterile container |
| SP61049 | AFB isolation by rapid culture using BACTEC MGIT Pus, abscess and aspirates | Automated BACTEC MGIT 960 | Pus in sterile container |
| SP60816 | AFB isolation by rapid culture using BACTEC MGIT Sputum | Automated BACTEC MGIT 960 | Morning sputum |
| SP63181 | AFB isolation by rapid culture using BACTEC MGIT Tissue / Biopsy | Automated BACTEC MGIT 960 | Tissue / biopsy in sterile container |
| SP60817 | AFB isolation by rapid culture using BACTEC MGIT Urine | Automated BACTEC MGIT 960 | Morning urine sample |
The skin test
The skin test is a widely used test for diagnosing TB. In countries with low rates of TB it is often used to test for latent TB infection. The problem with using it in countries with high rates of TB infection is that the majority of people may have latent TB.
The skin test involves injecting a small amount of fluid (called tuberculin) into the skin in the lower part of the arm. Then the person must return after 48 to 72 hours to have a trained health care worker look at their arm. The health care worker will look for a raised hard area or swelling, and if there is one then they will measure its size. They will not include any general area of redness.
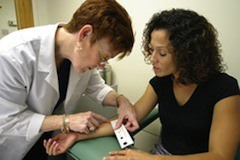 A health care worker measures the size of the reaction to the tuberculin skin test © CDC
A health care worker measures the size of the reaction to the tuberculin skin test © CDCThe test result depends on the size of the raised hard area or swelling. The larger the size of the affected area the greater the likelihood that the person has been infected with TB bacteria at some time in the past. But interpreting the TB skin test result, that is whether it is a positive result, may also involve considering the lifestyle factors of the person being tested for TB.2 The TB skin test also cannot tell if the person has latent TB or active TB disease.
The Mantoux TB test is the type of TB test most often used, although the Heaf and Tine tests are still used in some countries. None of these tests though will guarantee a correct result. False positive results happen with the skin test because the person has been infected with a different type of bacteria, rather than the one that causes TB. It can also happen because the person has been vaccinated with the BCG vaccine. This vaccine is widely used in countries with high rates of TB infection. False negative results particularly happen with children, older people and people with HIV.
48-72 hours for Reporting – MRP 225 RSDifferent skin tests:
| SP60480 | Mantoux Test (01 TU) Tuberculin test | PPD | 2 ml of serum |
| SP63940 | Mantoux Test (02 TU) Tuberculin test | PPD | 2 ml of serum |
| SP63941 | Mantoux Test (05 TU) Tuberculin test | PPD | 2 ml of serum |
| SP63942 | Mantoux Test (10 TU) Tuberculin test | PPD | 2 ml of serum |
TB Interferon gamma release assays (IGRAs)
The Interferon Gamma Release Assays (IGRAs) are a new type of more accurate TB test. In this context referring to an assay is simply a way of referring to a test or procedure.
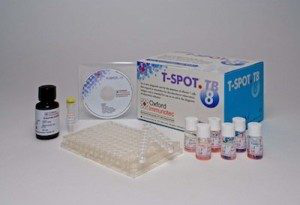 T-SPOT® TB Test © Oxford Immunotec
T-SPOT® TB Test © Oxford ImmunotecIGRAs are blood tests that measure a person’s immune response to the bacteria that causes TB. The immune system produces some special molecules called cytokines. These TB tests work by detecting a cytokine called the interferon gamma cytokine. In practice you carry out one of these TB tests by taking a blood sample and mixing it with special substances to identify if the cytokine is present.
Two IGRAs that have been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), and are commercially available in the U.S., are the QuantiFERON® TB Gold test, and the T-SPOT® TB test. The advantages of an IGRA TB test includes the fact that it only requires a single patient visit to carry out the TB test. Results can be available within 24 hours, and prior BCG vaccination does not cause a false positive result. Disadvantages include the fact that the blood sample must be processed fairly quickly, laboratory facilities are required, and the test is only for latent TB. It is also thought that the IGRAs may not be as accurate in people who have HIV. In low prevalence resource rich settings, IGRAs are beginning to be used in place of the TB skin test.
MRP – 2750 and Special Lab Rate: 1500 INRIGRA TB test:
| OT40474 | IGRAs (Interferon-Gamma Release Assay) QuantiFERON-TB Gold | ELISA | Blood in special container (lithium heparin) | Mon, Wed & Fri: 7 am |
Sputum smear microscopy
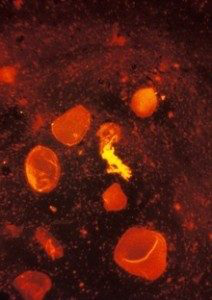 A sputum smear stained using fluorescent acid fast stain © CDC/R W Smithwick
A sputum smear stained using fluorescent acid fast stain © CDC/R W SmithwickSmear microscopy of sputum is often the first test to be used in countries with a high rate of TB infection. Sputum is a thick fluid that is produced in the lungs and the airways leading to the lungs. A sample of sputum is usually collected by the person coughing.
To test for TB several samples of sputum will normally be collected. In 2012 it was suggested that two specimens can be collected on the same day without any loss of accuracy.
To do the TB test a very thin layer of the sample is placed on a glass slide, and this is called a smear. A series of special stains are then applied to the sample, and the stained slide is examined under a microscope for signs of TB bacteria.
Sputum smear microscopy is inexpensive and simple, and people can be trained to do it relatively quickly and easily. In addition the results are available within hours. The sensitivity though is only about 50-60%.9 In countries with a high prevalence of both pulmonary TB and HIV infection, the detection rate can be even lower, as many people with HIV and TB co-infection have very low levels of TB bacteria in their sputum, and are therefore recorded as sputum negative.
Different sputum smear microscopy tests:| MB20472 | Sputum for AFB Test | Rapid AFB Cold Method | Sputum | Daily:12 pm | Reporting after 3 days | 220 |
| MB20503 | Sputum for AFB Test (3 Days) | Rapid AFB Cold Method | Sputum | Daily:12 pm | Reporting after 3 days | 550 |
| MB21067 | Sputum for AFB Test | Rapid AFB Cold Method | Sputum | Daily:12 pm | Reporting after 3 days | 935 |
| MB20513 | Sputum for Culture and Antibiotic Sensitivity | Aerobic culture & automated AST | Sputum | Daily:12 pm | Reporting after 3 days | 770 |
Fluorescent microscopy
The use of fluorescent microscopy is a way of making sputum TB tests more accurate. With a fluorescent microscope the smear is illuminated with a quartz halogen or high-pressure mercury vapour lamp, allowing a much larger area of the smear to be seen and resulting in more rapid examination of the specimen.
One disadvantage though is that a mercury vapour lamp is expensive and lasts a very short time. Such lamps also take a while to warm up, they burn significant amounts of electricity, and electricity supply problems can significantly shorten their life span. One way of overcoming these problems is the use of light emitting diodes (LEDs). These switch on extremely quickly, have an extremely long life, and they don’t explode.
In 2011 the World Health Organisation issued a policy statement recommending that conventional fluorescence microscopy should be replaced by LED microscopy. It also recommended that in a phased way, that LED microscopy should replace conventional Ziehl-Neelsen light microscopy.
Differen fluorescent microscopy tests:| SP70017 | AFB detection by smear examination Fluroscence Microscopy BAL & other respiratory samples | Flourescent stain and microscopy | Sterile leak-proof container | Daily: 9 am | Same day, 7 pm | 660 |
| SP70018 | AFB detection by smear examination Fluroscence Microscopy Body fluids | Flourescent stain and microscopy | Sterile leak-proof container | Daily: 9 am | Next day, 7 pm | 660 |
| SP70019 | AFB detection by smear examination Fluroscence Microscopy Pus, abscess and aspirates | Flourescent stain and microscopy | Sterile leak-proof container | Daily: 9 am | Next day, 7 pm | 660 |
| SP70020 | AFB detection by smear examination Fluroscence Microscopy Sputum - 1 sample | Flourescent stain and microscopy | Sterile leak-proof container | Daily: 9 am | Next day, 7 pm | 660 |
| SP70021 | AFB detection by smear examination Fluroscence Microscopy Sputum - 3 samples | Flourescent stain and microscopy | Sterile leak-proof container | Daily: 9 am | 4th day, 7 pm | 1600 |
| SP70022 | AFB detection by smear examination Fluroscence Microscopy Tissue and biopsy | Flourescent stain and microscopy | Sterile leak-proof container | Daily: 9 am | Next day, 7 pm | 660 |
| SP70023 | AFB detection by smear examination Fluroscence Microscopy Urine - 1 sample | Flourescent stain and microscopy | Sterile leak-proof container | Daily: 9 am | Next day, 7 pm | 660 |
| SP70024 | AFB detection by smear examination Fluroscence Microscopy Urine - 3 samples | Flourescent stain and microscopy | Sterile leak-proof container | Daily: 9 am | 4th day, 7 pm | 1600 |
| SP70025 | AFB detection by smear examination ZN Stain Sputum - 1 sample | ZN stain and microscopy | Sterile leak-proof container | Daily: 9 am and 3 pm | Next day, 7 pm | 220 |
| SP70026 | AFB detection by smear examination ZN Stain Sputum - 3 samples | ZN stain and microscopy | Sterile leak-proof container | Daily: 9 am and 3 pm | 3rd day, 7 pm | 550 |
Chest X-ray as a TB test
If a person has had TB bacteria which have caused inflammation in the lungs, an abnormal shadow may be visible on a chest X-ray. Also, acute pulmonary TB can be easily seen on an X-ray. However, what it shows is not specific. A normal chest X-ray cannot exclude extra pulmonary TB.
Also, in countries where resources are more limited, there is often a lack of X-ray facilities.
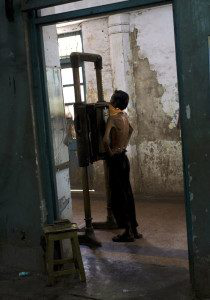 A man receives a chest X-Ray during the admission process at a hospital in India. © David Rochkind
A man receives a chest X-Ray during the admission process at a hospital in India. © David RochkindMRP 400 Special Discount Rate 375
Serological tests for TB
Serological tests for TB are tests carried out on samples of blood, and they claim to be able to diagnose TB by detecting antibodies in the blood. However, testing for TB by looking for antibodies in the blood is very difficult.
As a result serological TB tests, sometimes called serodiagnostic tests, for TB are inaccurate and unreliable. The World Health Organisation has warned that these tests should not be used to try and diagnose active TB. Some countries have banned the use of serological or serodiagnostic tests for TB.
Serological tests for TB are very different from the IGRA tests described above.
Different serological tests:| SP60947 | ADA Adenosine Deaminase Ascitic Fluid | Biochemical | 2 ml ascitic fluid in plain | Daily: 9 am to 1 pm | Next day, 7 pm | Used for diagnosing tuberculosis | 880 |
| SP60947 | ADA Adenosine Deaminase CSF | Biochemical | 2 ml CSF | Daily: 9 am to 1 pm | Next day, 7 pm | Used for diagnosing tuberculosis | 880 |
| SP60947 | ADA Adenosine Deaminase Pedicardial Fluid | Biochemical | 2 ml CSF | 2 ml pericardial fluid in plain | Next day, 7 pm | Used for diagnosing tuberculosis | 880 |
| SP60947 | ADA Adenosine Deaminase Peritoneal Fluid | Biochemical | 2 ml CSF | 2 ml peritoneal fluid in plain | Next day, 7 pm | Used for diagnosing tuberculosis | 880 |
| SP60947 | ADA Adenosine Deaminase Pleural Fluid | Biochemical | 2 ml CSF | 2 ml pleural fluid in plain | Next day, 7 pm | Used for diagnosing tuberculosis | 880 |
| SP60947 | ADA Adenosine Deaminase Pus | Biochemical | 2 ml CSF | Pus in sterile container | Next day, 7 pm | Used for diagnosing tuberculosis. Reference range not established. | 880 |
| SP60947 | ADA Adenosine Deaminase Serum | Biochemical | 2 ml serum | Pus in sterile container | Next day, 7 pm | Used for diagnosing tuberculosis | 880 |
Molecular tests for TB
Some new molecular tests such as the Genexpert test and the TrueNat test are now beginning to be available. Though they are too expensive to be widely used in many countries, the control of TB in South Africa is starting to show what is possible.
TB tests summary
There is no single test that can be used to test for TB in all circumstances. Some tests are cheap but not very accurate. Some can only be used to test for TB and cannot test for drug resistance. Others such as the TB culture test, the new Genexpert TB test and the TrueNat test can be used to diagnose TB and they can also test for some types of TB drug resistance.
With the development of the new molecular tests there is a beginning to significant progress in diagnosis. However it is unclear why the implementation of these tests cannot be faster. Although there are some issues about the speed with which patients are provided with treatment after receiving a diagnosis, faster diagnosis must surely be a key factor in controlling the TB epidemic in poor resource countries.
Drug susceptibility testing - Molecular tests, Line Probe Assay
What is drug susceptibility testing?
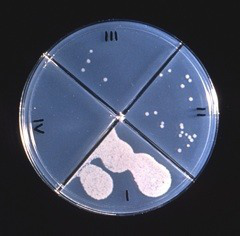 Agar culture plates reveal the results of a drug susceptibility test. © CDC
Agar culture plates reveal the results of a drug susceptibility test. © CDCDrug susceptibility testing means testing to find out if a person has got drug resistant TB. That means finding out which drugs the TB bacteria in their body are sensitive to. It is essential that if a person might possibly have drug resistant TB, that this is discovered as soon as possible, in order that the patient can be provided with effective TB treatment. Historically drug susceptibility testing has been done through culturing the bacteria. It has needed specific laboratory facilities and trained personnel. In addition it is a very lengthy process. There are however now some new tests available one of which is the Genexpert test. This is much easier to use, but it only provides limited information about drug resistance.
Different types of drug susceptibility tests
Drug susceptibility tests for TB are basically of two different types. One type of test is culture, which involves looking at how the bacteria behave. For example, do the bacteria grow in the presence of anti TB drugs? Another type of test involves looking at genetic mutations.
Molecular drug susceptibility tests
Since resistance arises from genetic mutations, this approach is to detect the mutations themselves. Many mutations associated with resistance have been identified and molecular tests to detect them have been developed. The advantages of molecular methods of drug susceptibility testing include rapid turnaround times, but the disadvantages include a low sensitivity for some compounds, and a major issue is cost.
It is generally perceived that specialist staff is required in order to perform molecular assays. However, some assays such as the Genexpert are extremely easy to use. They can even be taken out of the laboratory setting and used as a “near” point of care test.
Different molecular drug susceptibility tests:| SP70040 | AFB-MOTT antibiogram panel For rapid Growers Upto 10 drugs | Broth Microdilution | 5 ml of pure culture | Wed & Sat: 7:30 am | 15th day | Treatment history required. Identification of Mycobacterium species is compulsory prior to susceptibility testing. | 8250 |
| SP70041 | AFB-MOTT antibiogram panel For Slow growers Upto 10 drugs | Broth Microdilution | 5 ml of pure culture | Wed & Sat: 7:30 am | 15th day | Treatment history required. Identification of Mycobacterium species is compulsory prior to susceptibility testing. | 9350 |
| SP70043 | AFB-Mtb antibiogram Amikacin | Automated BACTEC MGIT 960 | 3-5 ml of pure culture (Mtb complex) | Daily: 7.30 am | Upto 4 weeks | Treatment history required. Request to be sent within 4 days of positive culture report. | 2640 |
| SP70044 | AFB-Mtb antibiogram Capreomycin | Automated BACTEC MGIT 960 | 3-5 ml of pure culture (Mtb complex) | Daily: 7.30 am | Upto 4 weeks | Treatment history required. Request to be sent within 4 days of positive culture report. | 2640 |
| SP70045 | AFB-Mtb antibiogram Clofazimine | Automated BACTEC MGIT 960 | 3-5 ml of pure culture (Mtb complex) | Daily: 7.30 am | Upto 4 weeks | Treatment history required. Request to be sent within 4 days of positive culture report. | 2640 |
| SP70046 | AFB-Mtb antibiogram Ethambutol | Automated BACTEC MGIT 960 | 3-5 ml of pure culture (Mtb complex) | Daily: 7.30 am | Upto 4 weeks | Treatment history required. Request to be sent within 4 days of positive culture report. | 2640 |
| SP70047 | AFB-Mtb antibiogram Ethionamide | Automated BACTEC MGIT 960 | 3-5 ml of pure culture (Mtb complex) | Daily: 7.30 am | Upto 4 weeks | Treatment history required. Request to be sent within 4 days of positive culture report. | 2640 |
| SP70048 | AFB-Mtb antibiogram Isoniazid | Automated BACTEC MGIT 960 | 3-5 ml of pure culture (Mtb complex) | Daily: 7.30 am | Upto 4 weeks | Treatment history required. Request to be sent within 4 days of positive culture report. | 2640 |
| SP70049 | AFB-Mtb antibiogram Kanamycin | Automated BACTEC MGIT 960 | 3-5 ml of pure culture (Mtb complex) | Daily: 7.30 am | Upto 4 weeks | Treatment history required. Request to be sent within 4 days of positive culture report. | 2640 |
| SP70050 | AFB-Mtb antibiogram Levofloxacin | Automated BACTEC MGIT 960 | 3-5 ml of pure culture (Mtb complex) | Daily: 7.30 am | Upto 4 weeks | Treatment history required. Request to be sent within 4 days of positive culture report. | 2640 |
| SP70051 | AFB-Mtb antibiogram Moxifloxacin | Automated BACTEC MGIT 960 | 3-5 ml of pure culture (Mtb complex) | Daily: 7.30 am | Upto 4 weeks | Treatment history required. Request to be sent within 4 days of positive culture report. | 2640 |
| SP70052 | AFB-Mtb antibiogram Ofloxacin | Automated BACTEC MGIT 960 | 3-5 ml of pure culture (Mtb complex) | Daily: 7.30 am | Upto 4 weeks | Treatment history required. Request to be sent within 4 days of positive culture report. | 2640 |
| SP70053 | AFB-Mtb antibiogram Pyrazinamide | Automated BACTEC MGIT 960 | 3-5 ml of pure culture (Mtb complex) | Daily: 7.30 am | Upto 4 weeks | Treatment history required. Request to be sent within 4 days of positive culture report. | 2640 |
| SP70054 | AFB-Mtb antibiogram Pyrazinamide | Automated BACTEC MGIT 960 | 3-5 ml of pure culture (Mtb complex) | Daily: 7.30 am | Upto 4 weeks | Treatment history required. Request to be sent within 4 days of positive culture report. | 2640 |
| SP70055 | AFB-Mtb antibiogram Rifabutin | Automated BACTEC MGIT 960 | 3-5 ml of pure culture (Mtb complex) | Daily: 7.30 am | Upto 4 weeks | Treatment history required. Request to be sent within 4 days of positive culture report. | 2640 |
| SP70056 | AFB-Mtb antibiogram Rifampicin | Automated BACTEC MGIT 960 | 3-5 ml of pure culture (Mtb complex) | Daily: 7.30 am | Upto 4 weeks | Treatment history required. Request to be sent within 4 days of positive culture report. | 2640 |
| SP70057 | AFB-Mtb antibiogram Streptomycin | Automated BACTEC MGIT 960 | 3-5 ml of pure culture (Mtb complex) | Daily: 7.30 am | Upto 4 weeks | Treatment history required. Request to be sent within 4 days of positive culture report. | 2640 |
| SP70058 | AFB-Mtb antibiogram panel 1st and 2nd Line panel 10 drugs | Automated BACTEC MGIT 960 | 5 ml pure culture bottle or tube | Daily: 7.30 am | Upto 4 weeks | Includes SIREP and 2nd Line (4 drugs) panel and Capreomycin | 10450 |
| SP70059 | AFB-Mtb antibiogram panel 1st Line (4 drugs) SIRE | Automated BACTEC MGIT 960 | 5 ml of pure culture | Daily: 7.30 am | Upto 4 weeks | Includes Streptomycin, Isoniazid, Rifampicin, Ethambutol | 5170 |
| SP70060 | AFB-Mtb antibiogram panel 2nd Line (4 drugs) KEPO | Automated BACTEC MGIT 960 | 5 ml of pure culture | Daily: 7.30 am | Upto 4 weeks | Includes Kanamycin, Ethionamide, PAS, Ofloxacin | 6380 |
| SP70061 | AFB-Mtb antibiogram panel Additional drugs - 4 nos. MACC | Automated BACTEC MGIT 960 | 5 ml of pure culture | Daily: 7.30 am | Upto 4 weeks | Includes Moxifloxacin, Amikacin, Capreomycin, Clofazamine | 6160 |
| SP70052 | AFB-Mtb antibiogram panel Comprehensive panel 13 drugs | Automated BACTEC MGIT 960 | Pure culture (Mtb complex) | Daily: 7.30 am | Upto 4 weeks | SIREP, 2nd Line 4 drugs and additional 4 drugs | 14300 |
Beacon Assays
Beacon assays detect M. tuberculosis complex and associated rifampicin resistance directly from sputum samples using ultra sensitive PCR. The Genexpert TB assay is an automated real time based system that has a number of advantages including the fact that it is a closed tube system. The WHO is encouraging the use of the Genexpert TB test, but it has a number of disadvantages including cost.
Different beacon assays:| MB43925 | GeneXpert-AFB | Real-Time PCR | Sputum | Daily: 12 pm | 2 Days | 2750 | Special lab rate 2000 |
| MB44734 | GeneXpert-AFB (Others Samples) | Real-Time PCR | Others | Daily: 12 pm | 2 Days | 3300 | Special lab rate 2500 |
Line Probe Assays
Line probe assays are tests that use PCR and reverse hybridization methods for the rapid detection of mutations associated with drug resistance. Line probe assays are designed to identify M. tuberculosis complex and simultaneously detect mutations associated with drug resistance. One of the disadvantages with these assays is that they have an open-tube format, which can lead to cross contamination and an increased risk of false positive results.
Different line probe assays (PCR):| SP70027 | AFB detection of DNA by Real-time PCR BAL and other respiratory samples | Real-time PCR | Full bronchial lavage in container | Daily: 7.30 am | Next day, 7 pm | Diagnosis of tuberculosis | 2750 |
| SP70028 | AFB detection of DNA by Real-time PCR Body Fluid | Real-time PCR | Body fluid in sterile container | Daily: 7.30 am | Next day, 7 pm | Diagnosis of tuberculosis | 2750 |
| SP70029 | AFB detection of DNA by Real-time PCR CSF | Real-time PCR | CSF in sterile container | Daily: 7.30 am | Next day, 7 pm | Diagnosis of tuberculosis | 2750 |
| SP70030 | AFB detection of DNA by Real-time PCR Pus, abscess and aspirates | Real-time PCR | Pus in sterile container | Daily: 7.30 am | Next day, 7 pm | Diagnosis of tuberculosis | 2750 |
| SP70031 | AFB detection of DNA by Real-time PCR Sputum | Real-time PCR | Morning sputum of 3 consecutive days | Daily: 7.30 am | Next day, 7 pm | Diagnosis of tuberculosis | 2750 |
| SP70032 | AFB detection of DNA by Real-time PCR Tissue and biopsy | Real-time PCR | Tissue in saline | Daily: 7.30 am | Next day, 7 pm | Diagnosis of tuberculosis | 2750 |
| SP70033 | AFB detection of DNA by Real-time PCR Urine | Real-time PCR | Morning urine sample of 3 consecutive days | Daily: 7.30 am | Next day, 7 pm | Diagnosis of tuberculosis | 2750 |
Line Probe Assay (LPA) technology is suitable for use at national/central reference laboratories, or at laboratories where there is proven capacity to conduct molecular testing. There must be adequate and appropriate laboratory infrastructure and equipment. This must also include the necessary biosafety precautions and the prevention of contamination. Appropriate laboratory staff also need to be trained to conduct LPA procedures.
Different line probe assays (Hain’s Test):| SP70038 | AFB MDR screen Hain's Line Probe Assay Extrapulmonary samples | Line probe assay (Hain's Test) | - | Mon : 9 am | 3rd day, 7 pm | 1980 | |
| SP70039 | AFB MDR screen Hain's Line Probe Assay Sputum, BAL, other respiratory samples | Line probe assay (Hain's Test) | Morning sputum of 3 consecutive days | Mon : 9 am | 3rd day, 7 pm | Done for both smear-positive and negative pulmonary samples / pure cultures | 1980 |
| SP70042 | AFB-MOTT Speciation Additional species by Hain's Line Probe Assay Pure culture | Line probe assay (Hain's Test) | 5 ml of pure culture | Mon & Thu: 9 am | Next day, 7 pm | 3750 | |
| SP70063 | AFB XDR Screen Hain's Line Probe Assay Extrapulmonary samples | - | Mon : 9 am | 3rd day, 7 pm | Test done for smear-positive pulmonary samples / pure cultures | 5500 | |
| SP70064 | AFB XDR Screen Hain's Line Probe Assay Sputum, BAL, other respiratory samples | Line probe assay (Hain's Test) | Morning sputum of 3 consecutive days | Tue: 9 am | Next day, 7 pm | Test done for smear-positive pulmonary samples / pure cultures | 5500 |